A month after announcing one of the largest data breaches ever, Yahoo is continuing to deal with the subsequent fallout and reputation damage related to that massive cyber theft.
On September 22, Yahoo confirmed that information associated with at least 500 million user accounts was stolen. The day after that breach announcement, Yahoo saw a 474 percent rise in online mentions, according to social media monitoring company BrandWatch — 70 percent of which were negative. Since then there’s been an ongoing swirl of negativity surrounding Yahoo’s breach — from lawsuits to concerned regulators to potential lost users — and that has led to reports that Verizon may either push for as much as a $1 billion reduction in its pending $4.8 billion agreement to buy Yahoo or back out of the deal altogether.
The negativity around the Yahoo brand due to its breach poses a difficult-to-answer question: just how much damage does a cyber-attack actually have on the bottom line of a company?
Difficulty of Tracking Brand Damage
Tracking brand damage directly tied to a cyber incident is a difficult prospect; however, there does appear to be at least one correlation. A survey conducted by SANS for a December 2015 paper, Cleaning Up After a Breach Post-Breach Impact: A Cost Compendium, found that “the breaches receiving the most media attention also suffered the greatest loss in brand/reputation.”
Which comes first in that chicken-or-egg scenario is up for debate, but SurfWatch Labs’ data suggests that, for the most part, it’s the scope and potential damage of breaches that drive the media coverage, not the other way around.
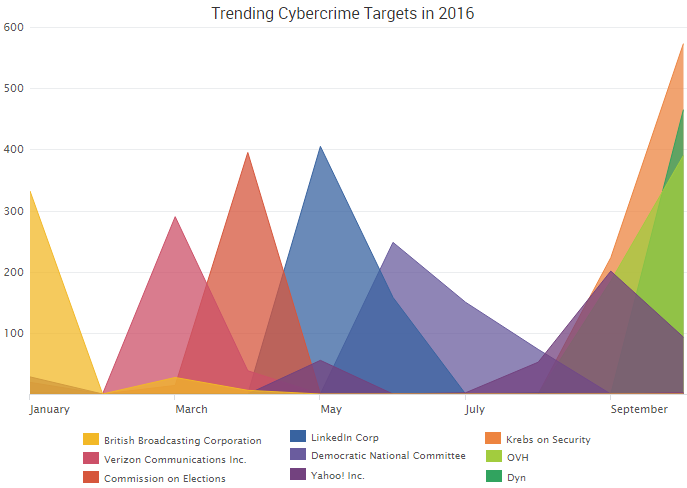
A quick glance at the list of the year’s top trending cybercrime events, based on the number of CyberFacts collected by SurfWatch Labs, shows that the most-discussed targets generally line up with the most widespread and impactful breaches: the Philippines Commission on Elections, LinkedIn, the Democratic National Committee, Yahoo and, more recently, targets of major DDoS attacks.
Other High-Profile Incidents Damage Brands
Like Yahoo, Wells Fargo is dealing with similar ongoing brand issues after reports of employees fraudulently opening more than two million customer accounts dominated several news cycles last month. A survey of 1,500 bank customers by management consultancy firm cg42 found that negative perceptions of Wells Fargo had spiked from 15 percent before the scandal to 52 percent afterwards. Likewise, the number of prospects that were very or extremely likely to consider doing business with Wells Fargo has plummeted from 21 percent to just three percent.
“The short and medium term outlook for Wells Fargo is gloomy, and the fallout from the scandal will impact the bank’s bottom line for years to come,” the report stated.
Wells Fargo is attempting to stem the tide with a new advertising campaign that promises, among other things, to begin proactively notifying customers of new accounts that are opened in their names. That campaign follows the firing of thousands of employees and the resignation of CEO John Stumpf.
Similar resignations have followed other high-profile breaches this year, most notably the breach at the Democratic National Committee, which lead to the resignations of chairwoman Debbie Wasserman Schultz, chief executive Amy Dacey, chief financial officer Brad Marshall and communications director Luis Miranda.
The brand damage from a cyber-attack can also move down to the supply chain, as we noted last week with XiongMai Technologies, a Chinese electronic company that makes products used in many of the Internet-connected DVRs and cameras tied to the massive DDoS attacks against Krebs On Security, OVH and Dyn. XiongMai said on Monday that it would issue a recall of some of its U.S. products. That recall notice also threatened legal action against individuals and organizations who “defame” the company with “false statements,” but the threat of legal action has been described by some as simply a face-saving PR effort by a company that’s used to operating behind the scenes and selling its white-labeled products to other brands.
Extent of Yahoo Fallout Uncertain
If the Yahoo breach will have a direct impact on its acquisition by Verizon is yet to be seen. Verizon’s general counsel Craig Silliman told Reuters and other reporters two weeks ago that the incident could trigger a clause in the deal that says Verizon can withdraw if a new event “reasonably can be expected to have a material adverse effect on the business, assets, properties, results of operation or financial condition of the business.”
“I think we have a reasonable basis to believe right now that the impact is material and we’re looking to Yahoo to demonstrate to us the full impact,” Silliman said, adding that Verizon needed to obtain “significant information” before making a final decision.
Like cg42 noted about Wells Fargo, the effects of a major cyber incident can take years to fully play out, and even then, it can be difficult to attribute some of the years-long business trends directly back to one cybercrime event.
One takeaway worth noting is that many of the major cybercrime stories that remain in the spotlight each year contain a similar thread: the lack of proactively addressing cyber risk. That seemingly cavalier attitude around cybersecurity is frequently cited by both data breach litigation and government and private regulators — and it will often prolong the a negative story with hearings, lawsuits and a string of news stories that continue to cause brand damage long after the initial incident occurred.


One thought on “Yahoo and Others Face Cybercrime-Related Brand Damage”