While new initiatives by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) are making it harder for cybercriminals to successfully file fraudulent tax returns, those measures have not slowed down the theft of employee W-2 information this year.
The SurfWatch Labs analyst team has observed groups of malicious actors sharing concerns about government efforts to combat fraud, as well as tips on how those protections can be circumvented, in several discussion threads on popular dark web markets. Several of those actors suggested teaming up with other seasoned cybercriminals in order to share tactics and improve their success rates in the face of the new measures. “We’re gonna have to join forces if we are going to beat the odds this year,” wrote one actor on a now-deleted tax fraud discussion thread. Another actor in a separate thread echoed those sentiments: “The process has become much more difficult over the past couple of years, but [it’s] still doable to some extent. Not like in the good ‘ole days though.”
Another actor expressed concern over new verification codes to be included on 50 million W-2 forms during the 2017 tax season — up from two million forms using the codes last year. “My guess is if this is successful, then within 2 years it will be on every W2,” the actor wrote.

The IRS has partnered with certain Payroll Service Providers this tax season to provide a 16-digit code designed to help verify the accuracy of millions of W-2s. However, as the IRS noted in its announcement, the verification rollout is only a test and “omitted and incorrect W-2 Verification Codes will not delay the processing” of returns filed this year. Other more tangible efforts to combat tax fraud include the IRS holding any refunds claiming the Earned Income Tax Credit or the Additional Child Tax Credit until February 15 to provide more time to verify the accuracy of returns, and the requirement of an individual’s date of birth and previous-year’s adjusted gross income when using tax software for the first time. Some states also ask for additional identification information, such as driver’s license numbers, in order to file their returns.
Additional anti-fraud efforts have come largely because of the large volume of fraudulent tax returns filed each year. Over the first nine months of 2015, the IRS confirmed that 1.2 million fraudulent tax returns made it into the agency’s tax return processing systems. Attempts to combat the massive amount of fraud resulted in 787,000 fraudulent returns over the same period in 2016 — a nearly 50 percent drop. It’s too early to say how 2017 will fare in terms of the number of fraudulent returns and the total cost to the IRS. What is clear is that cybercriminals are continuing to target tax-related information such as W-2s despite those changes — and they’re having great success.
As I’ve noted in other articles, cybercriminals follow the path of of least resistance and most profit. While cybercriminals face more resistance than in the past, their motivation, opportunity and capability are clearly still there.
Tax-related cybercrime is cyclical, and cyber threat intelligence around the subject peaks around this time every year. However, this past February was the most active month in terms of the volume of data SurfWatch Labs has collected around tax fraud since May 2015, and that spike in 2015 was due to a large amount of threat intelligence data surrounding the theft of taxpayer information from the IRS’ “Get Transcript” service.
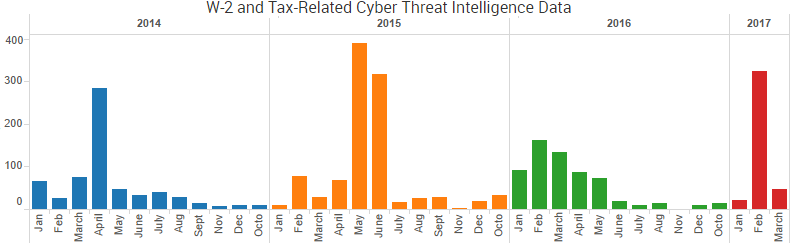
Much of the recent data directly relates to phishing incidents that have resulted in the theft of employee W-2 information. As we wrote in a blog early last month, malicious actors are using the same simple but effective phishing tactics that led to last year’s wave of successful W-2 thefts. This week we saw the number of organizations that have publicly confirmed breaches due to W-2 phishing surpass 100 for the year, and that number does not even include the numerous organizations that had W-2 information stolen through other means, such as data breaches or incidents at tax preparation firms or payroll providers.
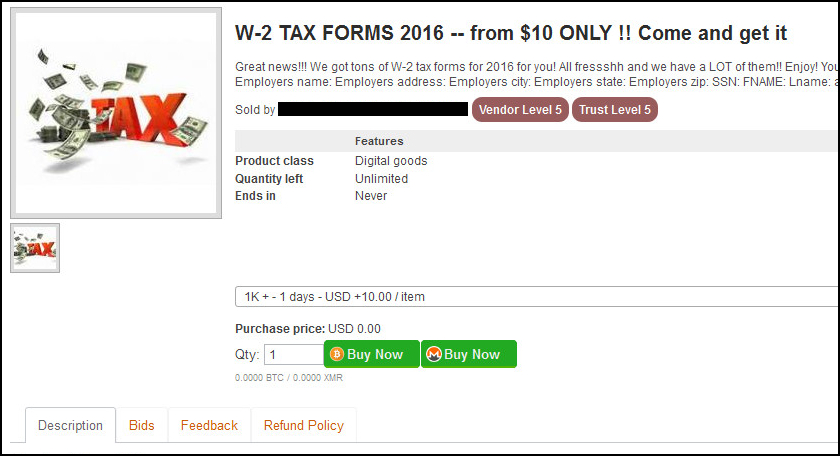
That stolen W-2 information is then used to file fraudulent tax returns, commit other forms of identity theft, or sold on various dark web markets for around $10 each. That can translate into a decent profit for a cybercriminal actor who can successfully dupe a handful of payroll or human resource employees into handing over hundreds — or thousands — of W-2 forms at a time.
But as we noted above, W-2 forms are now only part of the information needed to successfully dupe the IRS. Many returns will also need information such as the individual’s date of birth and previous year’s adjusted gross income. That information can be harder to come by, and how to best obtain that information is one of the key discussion points on the cybercriminal forums observed by our analysts.
“How do I get to know the AGI [Adjusted Gross Income]?” one actor asked the group in a discussion thread on a dark web forum. Another actor, who claims to have gone solo this year after previously being part of a group engaged in tax fraud, said information such as AGI generally requires other forms of data collection or social engineering. “You’ll have a tricky time getting it,” the actor warned. Later, the actor advised that AGI can often be found in an individual’s car note or home loan documentation.
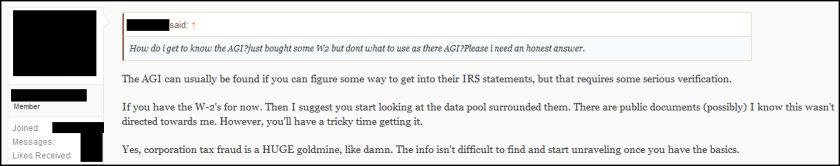
In a separate thread, the same actor wrote a long post that is part inspirational pep talk to wannabe fraudsters frustrated by the recent changes, part FAQ on how to best perform tax fraud. We won’t share the full details of that post here (including details such as which financial institutions and methods work best for receiving fraudulent tax return payments), as this post is meant to help illuminate the thought process of cybercriminals, not to serve as a walkthrough on how to successfully commit tax fraud. Nevertheless, the section on how to find an individual’s AGI is worth noting due to the lengths the actor claims to go — and may now need to go — in order to pull off a successful season of tax fraud.
The actor explained, “For everyone I targeted, I started researching them 6 months ago” by looking through public data for things like birth announcements (to “add that baby child credit”) or for minor offenses such as driving under the influence (to find people who have jobs “in the good bracket” that are also more likely to be “one of the last minute tax filers”).
“Lots of social engineering goes into this as well,” the actor wrote. “I have even been so bold to call some, pretending to solicit them into ‘free tax assistance’ [to] find out when they plan on filing.”

That extra legwork is why listings on dark web markets that include information such as AGI tend to sell at much higher prices than those without. For example, the listing below, which “contains all info needed for filing [a] tax refund,” was priced at $50, five times the price of a listing selling only stolen W-2 information.

These discussions indicate that efforts made by the IRS, financial institutions, and others have made the practice of filing fraudulent tax returns more difficult for cybercriminal actors. Despite those efforts, a number of tax-related breaches continue to occur and a great deal of effort continues to be made by malicious actors to successfully bypass those protections and steal a slice of that lucrative tax pie.
As one actor reminded everyone: “Tax fraud is a billion dollar entity. Take your cut along with the others. Don’t be dissuaded.”


One thought on “IRS and Cybercriminals Battle Over Billion Dollar Tax Fraud Industry”