I’ve previously written about the rise of extortion as an emerging trend for 2017, but if you didn’t want to take my word for it, you should have listened to the numerous warnings shared at this year’s RSA 2017. Cyber-extortion has become one of the primary cybersecurity-related issues facing organizations — and it appears to be here to stay.
My analyst team has researched cyber extortion and have found that malicious actors are not only engaging in these threat tactics, but they’re using the surging popularity of extortion and ransomware to target organizations with a variety of fake extortion demands and empty threats. We cover this topic in depth in our latest report, The Extortion Epidemic: Fake Threats on the Rise as Ransoms and Blackmail Gain Popularity.
In the graphic below I’ve noted some popular extortion threats, how actors carry out the threats and the impending results. Essentially they’re following the path of least resistance and most profit.
The Many Faces of Extortion: Popular Threats
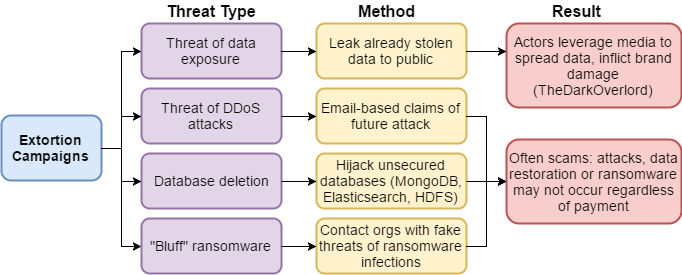
The gist of it all is that organizations have real fear around these threats and trust that bad actors have the ability to carry out these threats. Putting trust in bad guys is a bad idea!
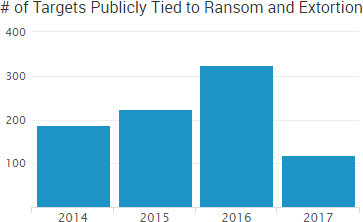
The fake ransoms are successful in large part because their real counterparts have impacted so many organizations. We’re already on pace to have more organizations publicly tied to ransoms and extortion in 2017 than any other year.
FBI officials have estimated the single subset of extortion known as ransomware to be a billion-dollar-a-year business, and fake ransomware threats have sprung up in the wake of that growth. A November 2016 survey of large UK businesses found that more than 40 percent had been contacted by cybercriminals claiming a fake ransomware infection. Surprisingly, two-thirds of those contacted reportedly paid the “bluff” ransom.
DDoS extortion threats are similarly low-effort cybercriminal campaigns, requiring only the sending of a threatening email. Earlier this month, Reuters reported that extortionists using the name “Armada Collective” had threatened Taiwanese brokerages with DDoS threats. Several of the brokerages experienced legitimate attacks following the threats; however, 2016 saw several campaigns leveraging the Armada Collective name where the threats were completely empty. One campaign generated over $100,000 in payments despite researchers not finding a single incident where a DDoS attack was actually made.
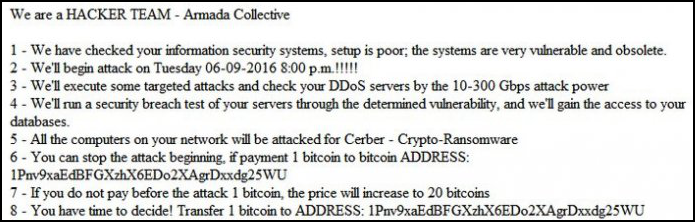
Extortion is also frequently tied to data breaches — both real and fake — as it is an another simple and direct avenue for cybercriminals to monetize stolen data. In January 2017 the E-Sports Entertainment Association (ESEA) was breached and the actor demanded a ransom payment of $100,000 to not release or sell the information on 1.5 million players.
ESEA said in its breach announcement that it did not pay the ransom because “paying any amount of money would not have provided any guarantees to our users as to what would happen with their stolen data.”
That is what reportedly happened to many of the victims who paid ransoms to have their hijacked MongoDB and other databases restored: they found themselves out both the data and the ransom payment. As noted in our report, it’s hard to have faith in cybercriminals, and organizations who do pay ransoms should be aware that in many cases those actors may not follow through after receiving extortion payments.
For more information on extortion threats and how to keep your organization safe, download the free report: The Extortion Epidemic: Fake Threats on the Rise as Ransoms and Blackmail Gain Popularity.
