Last month Aaron James Glende, 35, was arraigned in U.S. District Court in Atlanta on charges related to selling stolen bank account information on the Dark Web market AlphaBay. According to the indictment, Glende operated under the alias “IcyEagle” and began advertising his criminal services in late 2015.
Although the exact picture of how law enforcement managed track down and identify Glende remains unclear, the details released so far provide an interesting behind the scenes view of the cybercrime-related postings we often highlight on this blog.
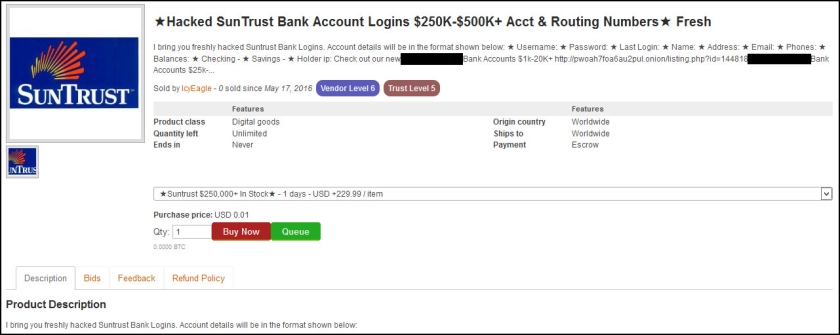
SurfWatch Labs has observed IcyEagle selling information related to a variety of companies over the past 10 months, but the June 28 indictment mentions only one company by name, SunTrust Bank.
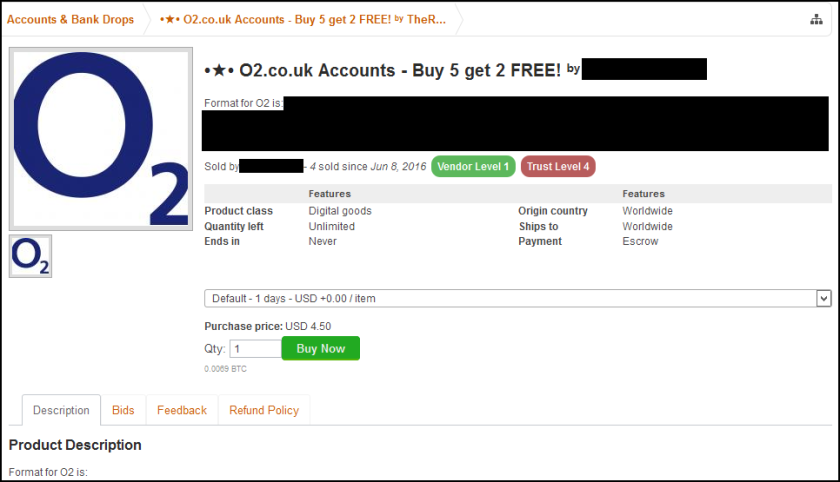
On multiple dates in March and April 2016, a Federal Bureau of Investigations (“FBI”) agent in the Northern District of Georgia, acting in an undercover capacity, accessed the AlphaBay website. While on the website, the agent purchased SunTrust account information from Icy Eagle using Bitcoin. A review of the information purchased from IcyEagle confirmed that it contained usernames, passwords, physical addresses, email addresses, telephone numbers, and bank account numbers that belonged to five different SunTrust Bank customers.
IcyEagle has listed SunTrust Bank accounts with a variety of balances this year, ranging from $250,000-$500,000 (selling for $229.99), to $100-$500 (selling for $9.99).
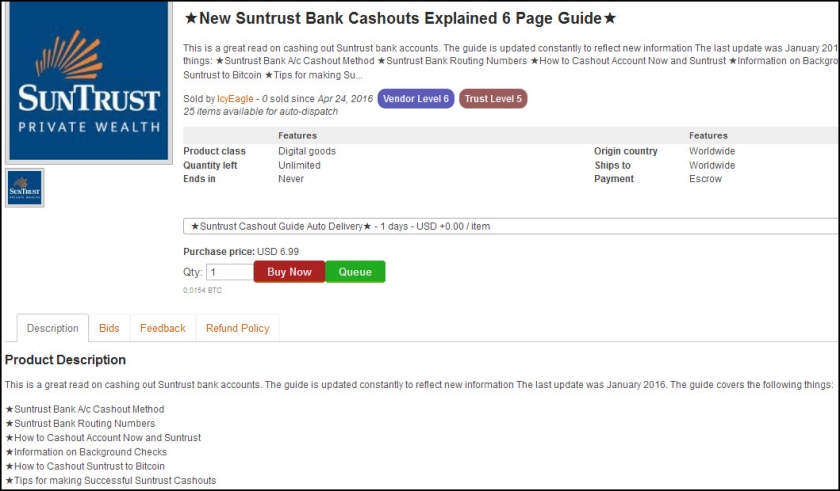
He also sold a 6-page guide on how to best cash out SunTrust Bank accounts, which includes sections on routing numbers, background checks, Bitcoin, and other tips.
“I bring you freshly hacked Sun Trust Bank Account Logins,” read one posting for SunTrust Bank accounts with balances between $30,000 and $150,000. “The accounts are notorious for having weak security.”
According to postings viewed by the FBI, IcyEagle sold at least 11 of these high-balance SunTrust Bank accounts and 32 of the lower-balance accounts.
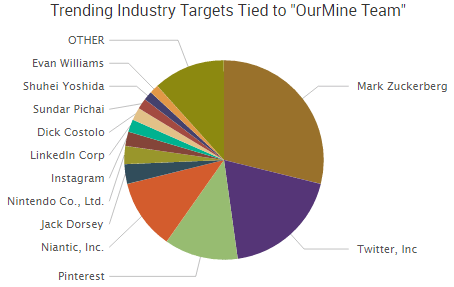
Dozens of other listings not-related to SunTrust Bank were also posted by IcyEagle and likely sold this year, although those were not listed in the recent indictment.
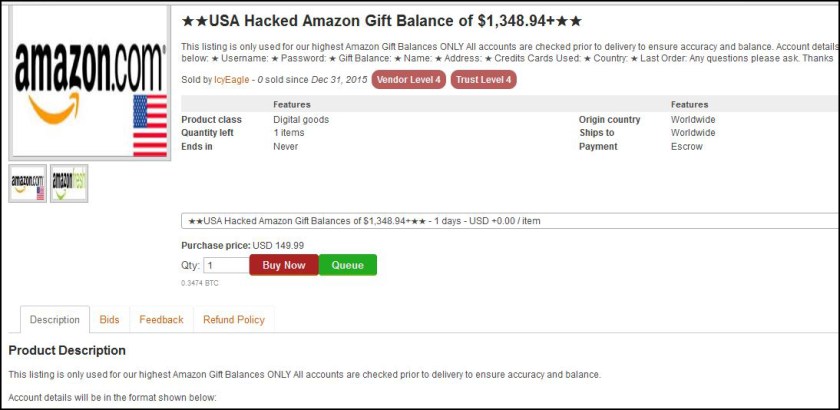
IcyEagle sold hacked Amazon gift balances for around one-tenth of the total balance. Other accounts for sale generally ranged from $2.99 to $14.99, depending on the type of account. These included email logins, dating website logins, customer reward program logins, logins for various financial services and more.
How was IcyEagle Caught?
An undercover officer purchased stolen bank account information from IcyEagle in March and April 2016, according to the indictment. Interestingly, Glende was also arrested by local police for selling drugs around the same time. A tip from U.S. Postal Inspectors led to police officers finding a “trove” of drugs at his Minnesota home in March.
“According to police, Postal inspectors reported finding packages connected to Glende that contained prescription pills,” wrote the Winona Post. “Officers executed a search warrant of Glende’s home on Friday, March 11, and reportedly found two U.S. Postal Service packages ready to be sent that contained the prescription narcotics Valium, Xanax, and oxycodone. Officers reportedly found a trove of other drugs at Glende’s home: nearly 600 Xanax pills, more than a dozen dextroampethamine capsules, 138 oxycodone pills, nearly 50 Valium pills, marijuana, and marijuana wax.”
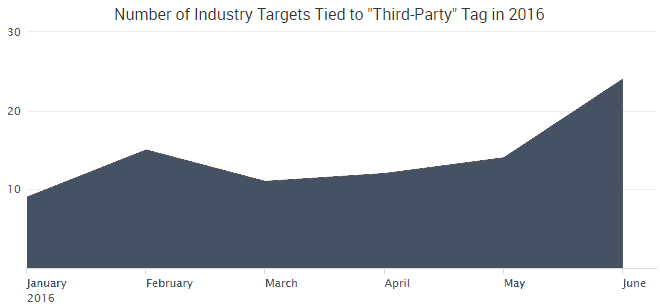
The indictment states that IcyEagle began advertising his criminal services by early November 2015. SurfWatch Labs’ data matches these allegations, with our threat intelligence analysts first observing several listings by IcyEagle in October 2015. New listings continued to be posted until the end of May, shortly before his arrest.
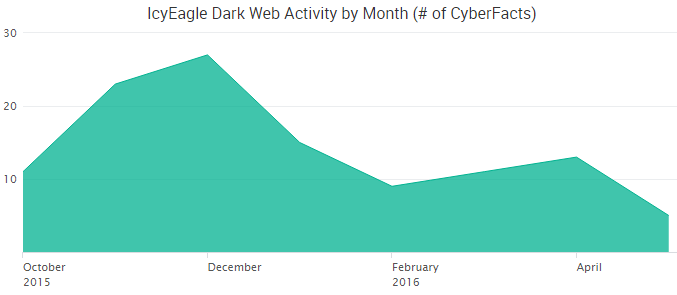
It’s unclear how — or even if — those two events are linked, but shortly after that drug-related arrest the FBI appears to have begun targeting IcyEagle’s postings on AlphaBay. We can speculate that after U.S. Postal Inspectors tied Glende to selling prescription drugs, the search warrant and subsequent investigation may have revealed evidence leading law enforcement to AlphaBay and IcyEagle — or vice versa. Either way, Glende is charged with performing cybercrime-related activities including five counts of bank fraud, four counts of aggravated identity theft, and one count of access device fraud.
Law enforcement officials continue to tout the arrests of alleged cybercriminals such as Glende as a sign that they will hold bad actors accountable for their actions despite the difficulties associated with such a task.
“The threat posed by cyber criminals is a persistently increasing problem for everyday citizens here in the U.S. and abroad,” said J. Britt Johnson, Special Agent in Charge, FBI Atlanta Field Office, in a press release. “This investigation and resulting arrest clearly illustrates that the FBI, however, will not cease in its effort to identify, locate, arrest and seek prosecution of these criminals regardless of how deep in the digital underground they reside.”
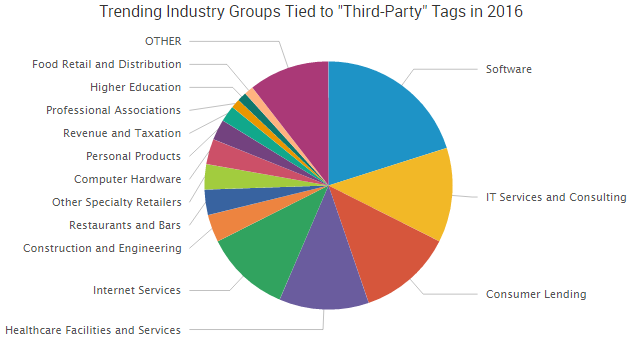
IcyEagle was just a drop in the bucket when compared to the thousands of pieces of Dark Web threat intelligence SurfWatch Labs analysts have recently observed. Nevertheless, cases like this serve as an important reminder of the insight that can be gained by watching these markets — not just for law enforcement, but for the companies that bear the brunt of this malicious cybercrime activity.










 of traditional insurance and then explain the difference between it and cyber-insurance. Traditionally, insurance is for tangible property – such as if you own a home, business, or rent space. You insure property against the risk of loss, and that property is typically tangible property. So, you’ll see language in first-party property insurance – which is insurance industry lingo for like your homeowner’s policy – that is set up to protect you from that. The core insuring agreement – in exchange for premium money – insures the risk of loss which is usually defined in terms as direct physical loss to tangible property.
of traditional insurance and then explain the difference between it and cyber-insurance. Traditionally, insurance is for tangible property – such as if you own a home, business, or rent space. You insure property against the risk of loss, and that property is typically tangible property. So, you’ll see language in first-party property insurance – which is insurance industry lingo for like your homeowner’s policy – that is set up to protect you from that. The core insuring agreement – in exchange for premium money – insures the risk of loss which is usually defined in terms as direct physical loss to tangible property.