The Dark Web is often misunderstood. For the unfamiliar, it is often viewed as either a mysterious place full of technological gurus communicating via primitive interfaces or else something akin to the Wild West — a no-holds-barred free-for-all of dangerous and illicit activity.
However, neither is the case.
The most popular marketplaces, where everything from stolen identities and credit cards to drugs and weapons are for sale, are more reminiscent of popular e-commerce sites than of the shady, backdoor dealings one may expect from criminals. Buying stolen accounts and intellectual property — as well as exploit kits, hacking-for-hire services, and the infrastructure to distribute malware is actually quite simple.
This reality runs contrary to much of the media coverage around the Dark Web. Stories such as the 2013 take down of the infamous Silk Road marketplace tend to focus on the scary aspects of “hidden” websites or scandalous details such as the Silk Road’s murder-for-hire plot — ignoring the fact that most people with an hour of free time and a few Google searches can easily find these sites and purchase illicit goods and services if desired.
In this series of blog posts, SurfWatch Labs hopes to shine on light on various aspects of the Dark Web, starting with what the Dark Web actually is — and what it isn’t.
1. Most Dark Web Markets are Customer Friendly
Those new to the Dark Web are often surprised by the level of customer service and the ease of which fraudulent goods and services can be obtained. However, this makes sense given the fact there are many competing marketplaces on the Dark Web. Customers and sellers are going to gravitate towards markets that appear the safest and have the best features.
AlphaBay is among the most popular and established Dark Web marketplaces (Nucleus Market, another popular marketplace, recently went offline). These marketplaces try to emulate the features seen on popular e-commerce sites such as Amazon or eBay.
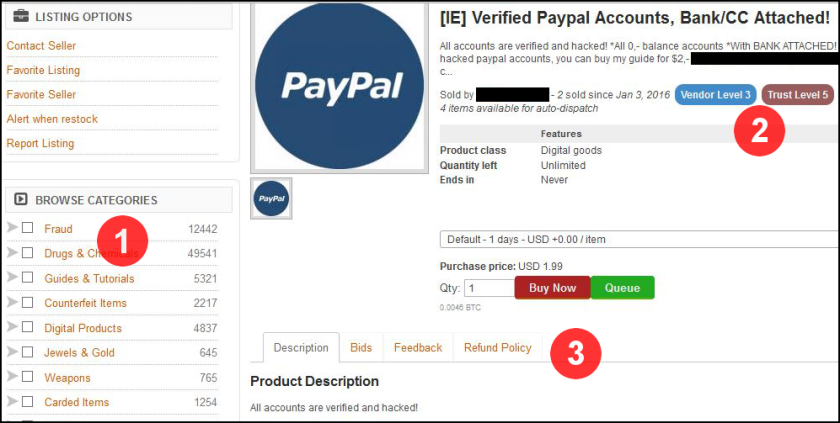
Some of these features include:
- Easy Navigation – Items are categorized into high-level categories such as fraud with subcategories like accounts, credit cards, personal information, data dumps and others.
- Vendor and Trust Levels – Sellers often have ratings. In the case of AlphaBay there is both a “Vendor Level,” which is based on number of sales and amount sold, and a “Trust Level,” which is based on the level of activity within the community as well as feedback from users.
- Feedback and Refunds – Buyers can also see feedback from customers and often have the option of returns or replacements such as credit card numbers that may no longer work due to being reported stolen.
Although these Dark Web markets tend to not be discoverable through Google and often require special software such as the Tor browser in order to access, they do want users to find and use them — so they are easy to locate, search for goods or services and make purchases.
2. They’re Concerned About Security and Trust
Most people know the old adage “there is no honor among thieves,” and these illicit markets work hard to help assuage those fears. This begins at the customer level with ratings and reviews.

These features help to establish trust when buying things like malware and stolen credit cards. Through ratings and feedback the community can collectively judge whether the items for sale can be used for legitimate fraud and attacks – or if they are just a scam.
In fact, these markets are actively trying to combat spammers and other bad actors just like e-commerce sites on the surface web. In March AlphaBay announced that they were rolling out mandatory two-factor authentication. As Motherboard’s headline ironically noted, “Some Dark Web Markets Have Better User Security than Gmail, Instagram.”
“We now enforce mandatory 2FA (two-factor authentication) for all vendors,” read the AlphaBay announcement. “This is part of an increasing effort to stop phishing on the marketplace. We recommend that everyone uses 2FA for more security.”
In addition, many markets try to avoid coming to the attention of law enforcement. Following the November 2015 terrorist attacks in Paris, which killed 130 people, Nucleus Market posted this message on its homepage:

The decision came just a week after the shootings and news reports that the guns used in the attacks may have been acquired from the Dark Web. Likewise, although child pornography is prevalent on the Dark Web, most of the markets do not sell it alongside the drugs, counterfeit goods and other illegal stolen items because that would attract unwanted attention to them and their user base.
Some Dark Web markets combat the the influx of law enforcement and researchers by requiring a referral in order to gain access. Others only show items that are for sale to established users or require authorization from the seller to view details about the product. This can make it harder for agents posing as “new customers” to monitor activity, and it helps to increase the trust factor around those marketplaces and forums.
3. No, the Dark Web is Not That Massive
In the summer of 2015, two researchers set an automated scanning tool loose on the Tor Network in an effort to find vulnerabilities on Dark Web sites. After just three hours the scan was over and they’d uncovered a little more than 7,000 sites.
A more recent effort to index the Dark Web put that number at close to 30,000 sites — a sizeable amount, but still far less than the massive underground world many have described.
As Wired wrote last year, the number of people on the Dark Web is quite small:
The Tor Project claims that only 1.5 percent of overall traffic on its anonymity network is to do with hidden sites, and that 2 million people per day use Tor in total. In short, the number of people visiting the dark web is a fraction of overall Tor users, the majority of whom are likely just using it to protect their regular browsing habits. Not only are dark web visitors a drop in the bucket of Tor users, they are a spec of dust in the galaxy of total Internet users.
4. It’s a Valuable Source of Threat Intelligence
The Dark Web is a valuable place to gather threat intelligence. SurfWatch Labs threat intelligence analysts proved that recently when they uncovered a breach into web hosting provider Invision Power Services.
That’s not to say everyone should jump on the Dark Web and poke around. It is easy to stumble across illegal things such as child pornography, and without the proper precautions companies or individuals may end up infecting their computers or putting themselves on the radar of cybercriminal groups — making themselves a potential target. However, what better way is there to understand the current threat landscape and the motivations of these malicious actors than to see for yourself what they are talking about, what they are selling, and if your company — or anyone in your supply chain — is being mentioned.
The Dark Web isn’t the cybersecurity cure-all that some companies make it out to be, but it is a significant part of a complete threat intelligence operation. Without visibility into these markets and the active threats they contain, your organization is operating at a disadvantage.


2 thoughts on “Dark Web Insights: Misconceptions About the Dark Web”