Several cryptocurrency exchanges were among the week’s top trending cybercrime targets due to a variety of different currency thefts, data breaches, and warnings from researchers.
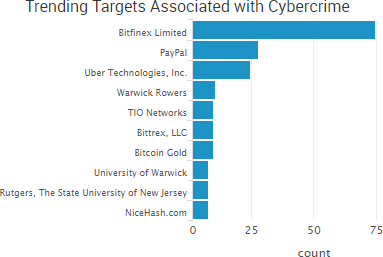
The most impactful incident occurred at the bitcoin mining platform and exchange NiceHash, which said on Wednesday that its payment system was compromised and the bitcoin in its wallet was stolen. NiceHash said it is “working to verify the precise number of BTC taken”; however, news outlets reported that a wallet linked to the attack obtained around 4,736 bitcoin, which is valued at more than $72 million based on Saturday’s price. The company has not released many details about the attack other than that it began after an employee’s computer was compromised.
In addition, researchers warned this week that the increased valuation of bitcoin has led to it becoming one of the top 10 most targeted industries for DDoS attacks. On Monday, Bitfinex said that its services were disrupted by a DDoS attack. On Thursday, Coinbase warned that the explosion of interest in digital currencies was creating “extreme volatility and stress” on its systems and warned its users to invest responsibly as any future downtime could impact their ability to trade.
News outlets also reported that some Bittrex customers who go through the company’s manual verification process but are rejected have received customer support emails that contain the passports details and photographs of other users, although Bittrex has not confirmed the reports.
Finally, the SEC announced that it obtained an emergency asset freeze to halt the Initial Coin Offering PlexCorps after it raised up to $15 million from thousands of investors by falsely promising a 13-fold profit in less than a month’s time.
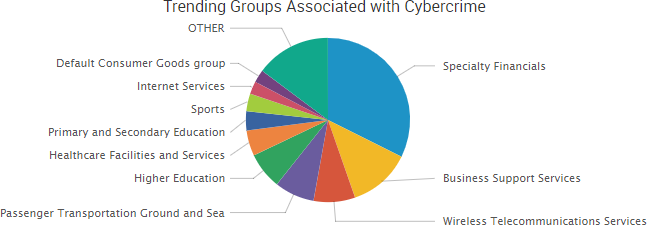
Other trending cybercrime events from the week include:
- TIO Networks announces breach: PayPal announced a breach at TIO Networks, a payment processor it acquired in July, that affects approximately 1.6 million customers. City Utilities (CU) and Duke Energy have since notified customers that their personal information was compromised due to the breach, as TIO was the provider of the operating system for CU’s payment kiosks and mobile payment app, in addition to being used to process Duke Energy’s in-person payments.
- Payment card breaches: The Image Group is notifying customers of a temporary vulnerability on its eCommerce platform, Payflow Pro, that made some payment card numbers susceptible to interception while in transit to PayPal. JAM Paper & Envelope is notifying customers of a payment card card breach affecting its website due to unauthorized access by a third party. A payment card breach involving the Royal National Institute for the Blind’s web store affects as many as 817 customers, and around 55 individuals have already reported fraudulent activity as a result of the incident.
- Extortion attacks: The Alameda County Library is notifying its users that their personal information may have been compromised after it received an extortion email that claimed hackers had gained access to the library’s entire database of users and may sell that information if they weren’t paid a five bitcoin ransom. The Mecklenburg County government in North Carolina said that its computer systems were infected with ransomware that is demanding $23,000 for the encryption key. Mad River Township Fire and EMS Department in Ohio said that years of data related to residents who used EMS or fire services was lost due to a ransomware infection. The fertility clinic CCRM Minneapolis said that nearly 3,300 patients may have had their information compromised due to a ransomware attack.
- Other notable incidents: The Center for Health Care Services in San Antonio is notifying 28,434 patients that their personal information was stolen by a former employee. The County of Humboldt is notifying current and former employees that the Humboldt County Sheriff’s Office recovered payroll documents from the county. Pulmonary Specialists of Louisville is notifying patients their information may have been compromised due to possible unauthorized access. Virtual keyboard developer Ai.Type, bike sharing company oBike, Real Time Health Quotes, and Stanford University all had data breaches due to accidental data exposure. Baptist Health Louisville, Sinai Health System, and The Henry Ford Health System notified patients of employee email account breaches.
- Law enforcement actions: Authorities reportedly shut down Leakbase, a service that sold access to more than two billion credentials collected from old data breaches. The Justice Department announced a software developer at the National Security Agency’s Tailored Access Operations has pleaded guilty to removing classified NSA data and later having that data stolen from his personal computer by Russian state-sponsored actors. A Michigan man pleaded guilty to gaining access to the Washtenaw County computer network and altering the electronic records of at least one inmate in an attempt to get the inmate released early. A Missouri man has been sentenced to six years in prison for hacking his former employer, American Crane & Tractor Parts, in order to steal trade secrets.
SurfWatch Labs collected data on many different companies tied to cybercrime over the past week. Some of those “newly seen” targets, meaning they either appeared in SurfWatch Labs’ data for the first time or else reappeared after being absent for several weeks, are shown in the chart below.

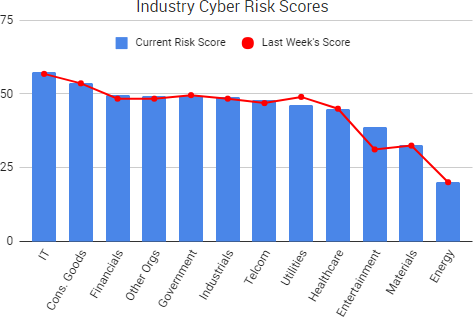
Cyber Risk Trends From the Past Week
 Phishing concerns were highlighted once again this past week due to a newly announced vulnerability that allows malicious actors to spoof emails, as well as warnings that phishers are making efforts to appear more legitimate.
Phishing concerns were highlighted once again this past week due to a newly announced vulnerability that allows malicious actors to spoof emails, as well as warnings that phishers are making efforts to appear more legitimate.
A researcher has discovered a collection of bugs in email clients, dubbed “Mailsploit,” that circumvents spoofing protection mechanisms and, in some cases, allows code injection attacks. The vulnerabilities were found in dozens of applications, including Apple Mail, Mozilla Thunderbird, Microsoft Outlook 2016, Yahoo! Mail, ProtonMail, and others.
The bug has been fixed in 10 products and triaged for 8 additional products, the researcher said. In addition, Mozilla and Opera said they won’t fix the bug as they consider it to be a server-side problem; however, Thunderbird developer Jörg Knobloch told Wired that a patch would be made available. DMARC spoofing protection is not attacked directly using Mailsploit, the researcher said, but rather bypassed by taking advantage of how the clients display the email sender name.
In addition, researchers said that nearly a quarter of all phishing websites are now hosted on HTTPS domains, up from three percent a year ago. The increase is due to both an increased number of HTTPS websites that can be compromised and used to host malicious content, as well as phishers registering HTTPS domains themselves due to their belief that the “HTTPS” designation makes a phishing site seem more legitimate to potential victims. An informal poll conducted by PhishLabs found that more than 80% of the respondents incorrectly believed the green padlock associated with HTTPS websites indicated that a website was either legitimate or safe — when in reality it only means that the connection is encrypted.
Individuals and organizations should be aware that malicious actors continue to leverage exploits like Mailsploit along with more secure-looking websites in order to dupe potential victims via phishing attacks with the goal of installing malware, gaining access to networks, or stealing sensitive data.








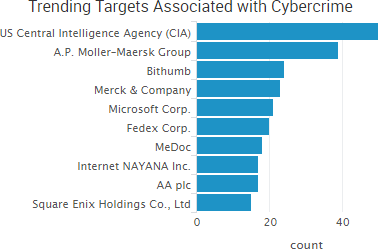


 Russian state-sponsored hackers are responsible for recent cyber-intrusions into the business systems of U.S. nuclear power plants and other energy companies, government officials said. It is the first time Russian government hackers are known to have compromised the networks of U.S. nuclear plants, the officials added.
Russian state-sponsored hackers are responsible for recent cyber-intrusions into the business systems of U.S. nuclear power plants and other energy companies, government officials said. It is the first time Russian government hackers are known to have compromised the networks of U.S. nuclear plants, the officials added.




