This week’s biggest story is the Cloudflare software bug discovered by Google researchers and disclosed Thursday that could have compromised private information such as HTTP cookies, authentication tokens, HTTP POST bodies, and other sensitive data.
 “The bug was serious because the leaked memory could contain private information and because it had been cached by search engines,” wrote John Graham-Cumming, the CTO of Cloudflare, which provides performance and security services to numerous major websites. “We have also not discovered any evidence of malicious exploits of the bug or other reports of its existence.”
“The bug was serious because the leaked memory could contain private information and because it had been cached by search engines,” wrote John Graham-Cumming, the CTO of Cloudflare, which provides performance and security services to numerous major websites. “We have also not discovered any evidence of malicious exploits of the bug or other reports of its existence.”
The bug was discovered by researcher Tavis Ormandy on February 17, and the data leakage may date back to September 22. However, the greatest period of impact was between February 13 and February 18 “with around 1 in every 3,300,000 HTTP requests through Cloudflare potentially resulting in memory leakage,” the company said. Popular services such as Uber, 1Password, FitBit, OkCupid, and many more use Cloudflare. Uber told media outlets the impact on its customers is minimal since “very little Uber traffic actually goes through Cloudflare,” and 1Pass said the company “designed 1Password with the expectation that SSL/TLS can fail” exactly for these types of incidents.
Days before the public disclosure, Ormandy wrote: “I’m finding private messages from major dating sites, full messages from a well-known chat service, online password manager data, frames from adult video sites, hotel bookings. We’re talking full HTTPS requests, client IP addresses, full responses, cookies, passwords, keys, data, everything.” Then in another comment, “We’re still working on identifying data that needs to be purged from caches.”
As Wired reported, efforts to discover any leaked data that has been cached and not yet scrubbed “has become something of an internet-wide scavenger hunt.”
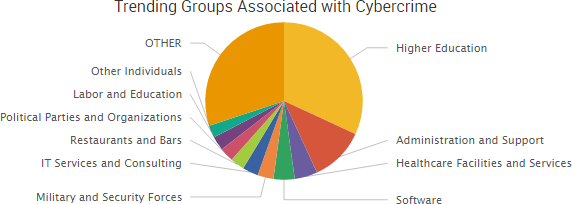
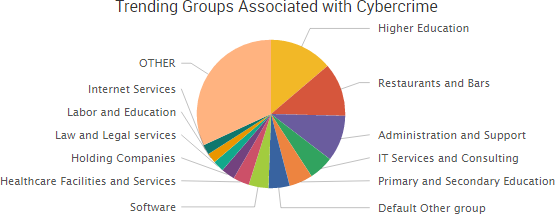
Other trending cybercrime events from the week include:
- Presidential campaign website defaced: A hacker going by the name “Pro_Mast3r” defaced a presidential campaign website for Donald Trump with a message that read, in part, “Peace From Iraq.” The hacker told Brian Krebs that he exploited a DNS misconfiguration to assume control of secure2.donaldjtrump.com.
- New databases continue to be sold on the dark web: An actor using the name “Berkut” is selling a database of 950,000 user accounts for the website of the music festival Coachella that was allegedly stolen this month. Motherboard confirmed the legitimacy of the database, which contains email addresses, usernames, and hashed passwords. The $300 listing claims that 360,000 of the accounts are related to the main Coachella website and the other 590,000, which contain additional information such as IP addresses, are related to the message board.
- Employees and students access sensitive data: Dignity Health St. Joseph’s Hospital and Medical Center is notifying approximately 600 patients that a part-time hospital employee viewed portions their medical records without a business reason between October 1, 2016, and November 22, 2016. An Ohio Department of Taxation employee was fired for accessing the confidential tax information of relatives and acquaintances dozens of times. A student of the South Washington County school district in Minnesota hacked into the district’s server and downloaded the data of more than 15,000 people to an external hard drive in January.
- Cybercrime-related arrests and sentencing: On Wednesday, February 22, UK law enforcement announced the arrest of a 29-year old British man charged with suspicion of carrying out the cyber attack against Deutsche Telekom in November of last year, which impacted up to 900,000 customers of the ISP. SurfWatch Labs analysts have moderate confidence that this individual is the hacker known as “Bestbuy,” and additional researchers have said the actor also used the alias “Popopret.” A former systems administrator for Georgia-Pacific was sentenced to 34 months in prison and ordered to pay damages of more than $1 million after pleading guilty to remotely accessing the plant’s computer system and intentionally transmitting code and commands designed to cause significant damage to Georgia-Pacific and its operations.
- Other cybercrime announcements: The personal information of 55 million voters in the Philippines was compromised when a computer from the Office of the Election Officer in Wao, Lanao del Sur was stolen, but the data was encrypted using the AES-256 protocol. A spear phishing campaign against individuals in the Mongolian government used the popular remote access tool Poison Ivy as well as two publicly available techniques to evade AppLocker application whitelisting, four stages of PowerShell scripts to make execution difficult to trace, and decoy documents to minimize user suspicion. The Texas Department of Transportation said a breach of its automated administrative system affected a small number of employees whose information was compromised and potentially altered. Actress Emily Ratajkowski is the latest celebrity to have an iCloud account containing sensitive information hacked.
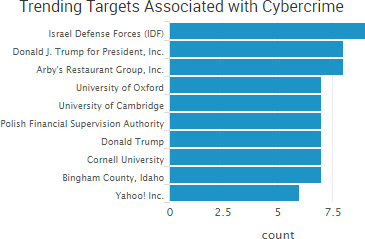
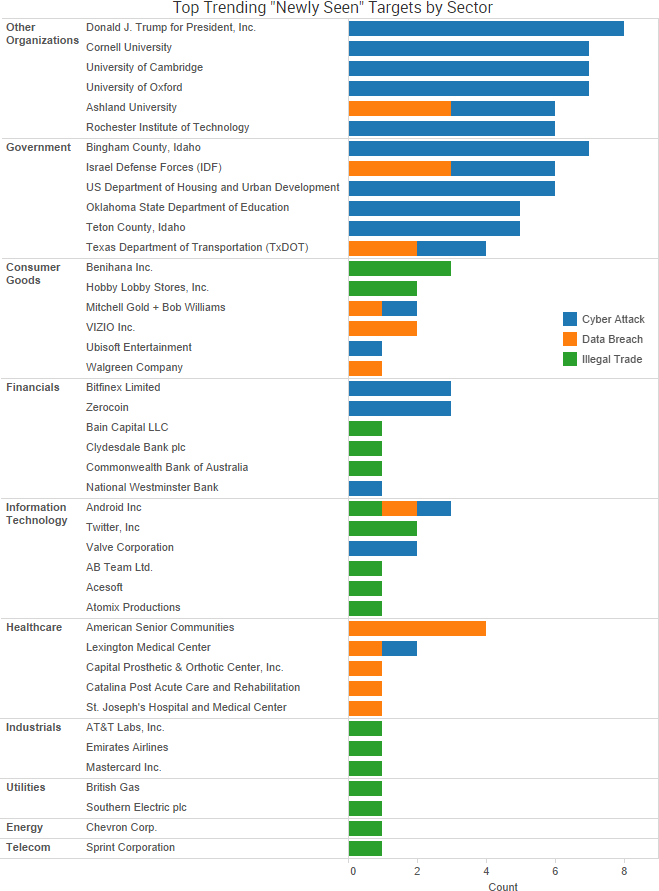
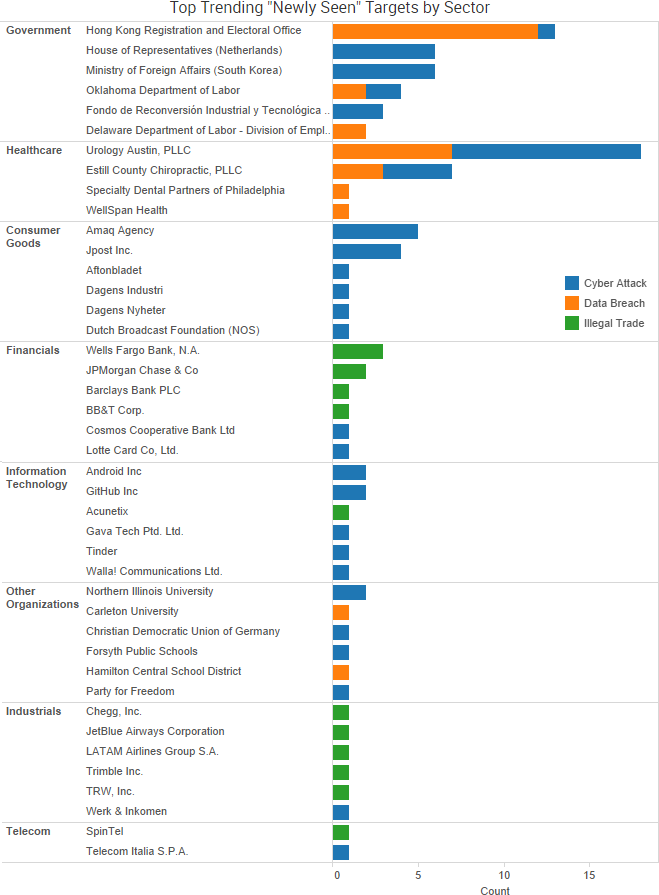
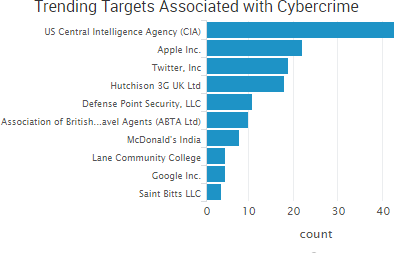
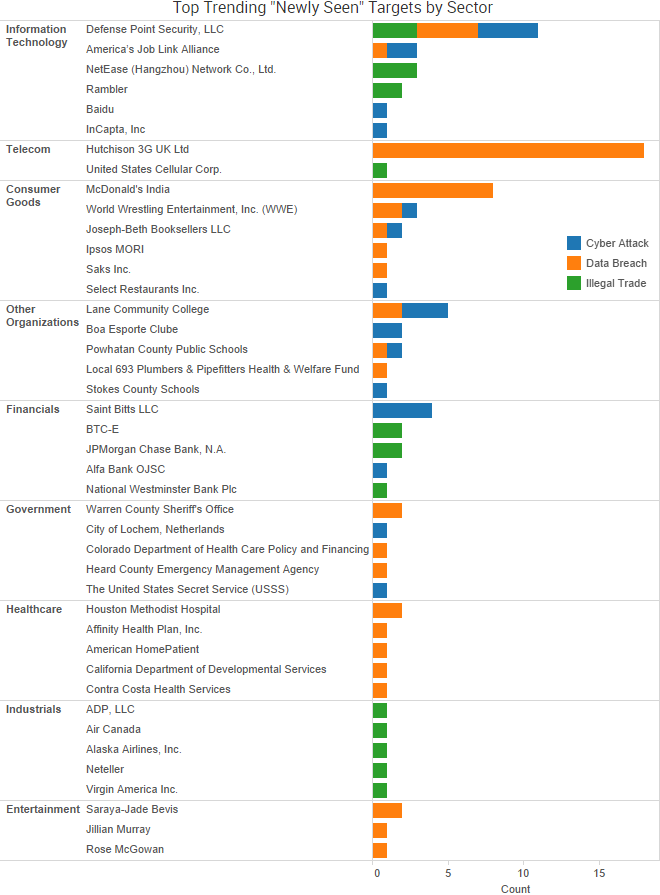
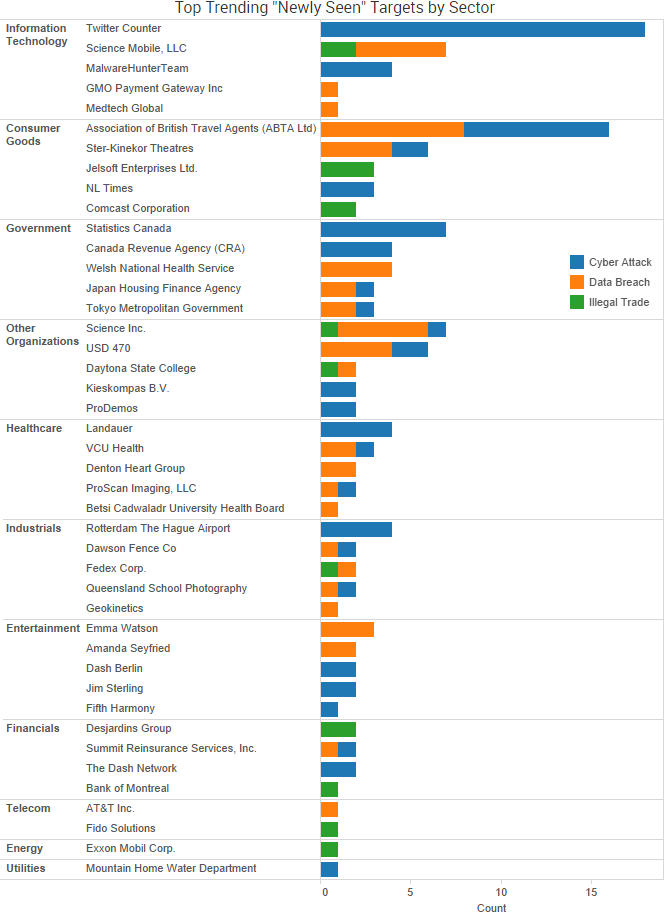
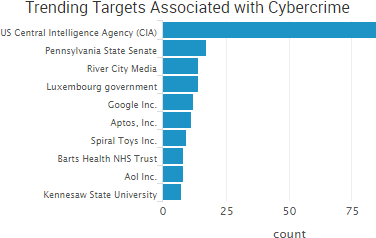
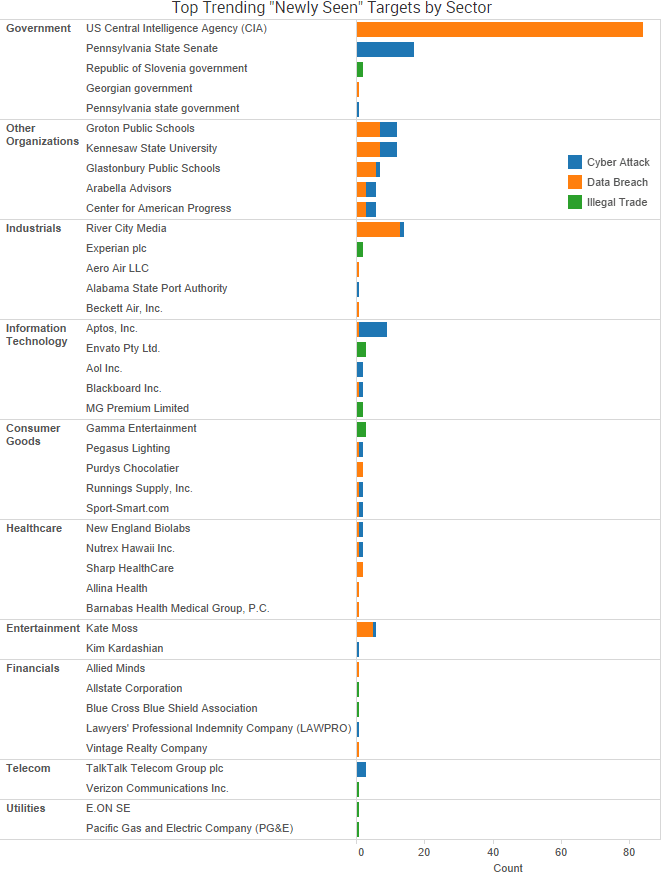
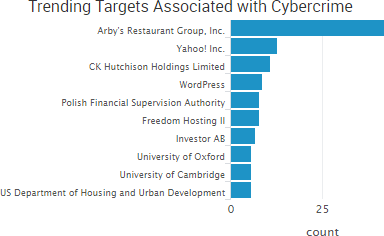
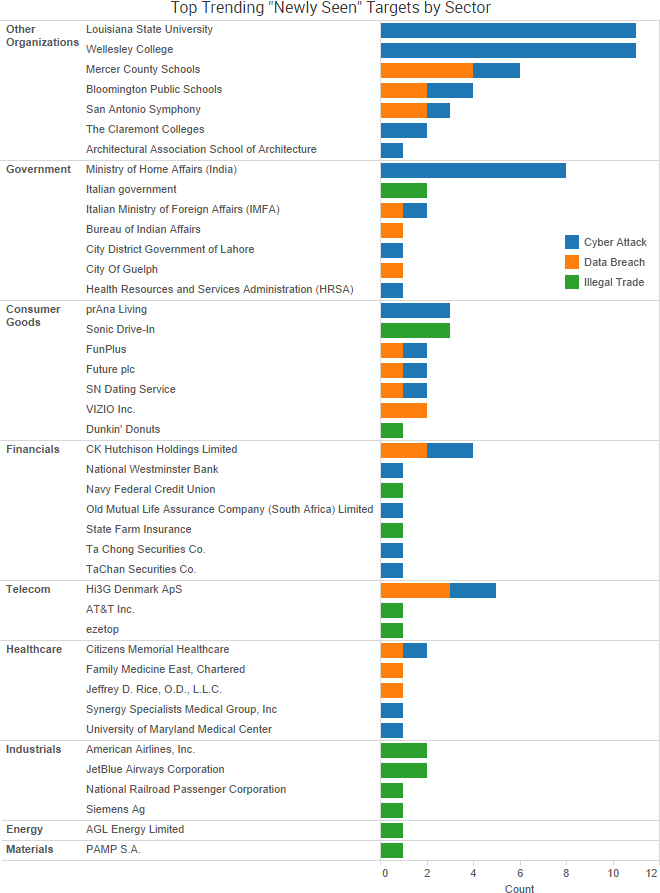
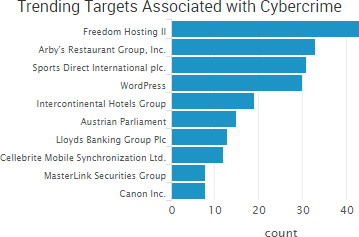
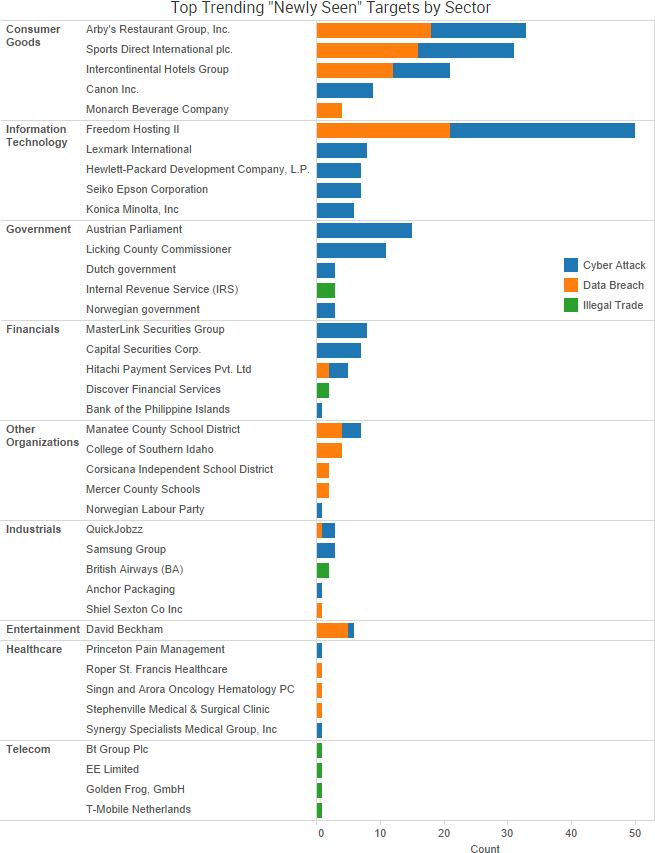
SurfWatch Labs collected data on many different companies tied to cybercrime over the past week. Some of those “newly seen” targets, meaning they either appeared in SurfWatch Labs’ data for the first time or else reappeared after being absent for several weeks, are shown in the chart below.
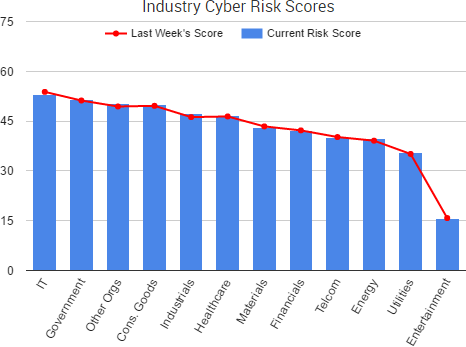
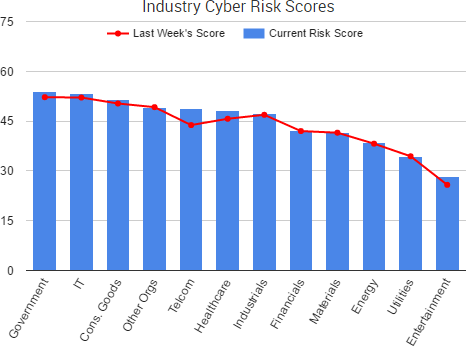
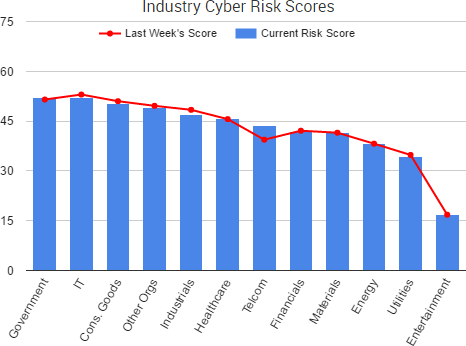
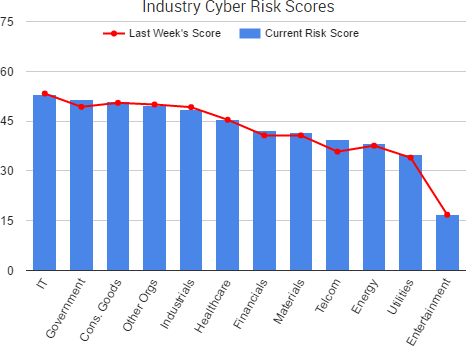
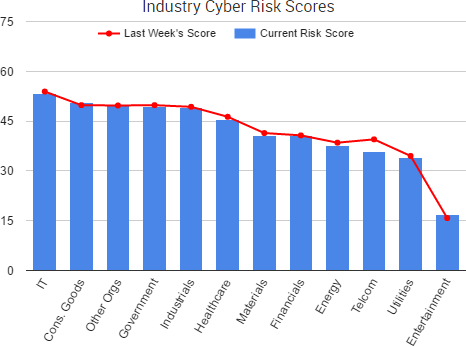
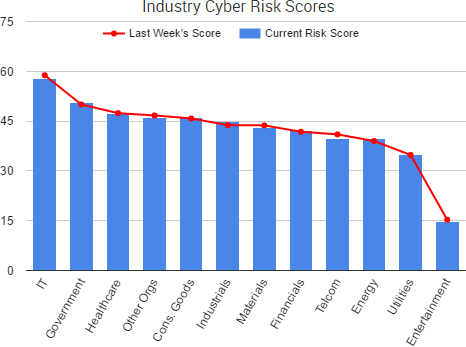
Cyber Risk Trends From the Past Week
 The Cloudflare bug can be traced back to a single character of code, which resulted in a buffer overrun, the company said.
The Cloudflare bug can be traced back to a single character of code, which resulted in a buffer overrun, the company said.
“The Ragel code we wrote contained a bug that caused the pointer to jump over the end of the buffer and past the ability of an equality check to spot the buffer overrun,” Graham-Cumming said. “Had the check been done using >= instead of == jumping over the buffer end would have been caught.”
Cloudflare wasn’t the only company to face issues due to a single character. Zerocoin announced last Friday that a a typographical error of a single additional character in code allowed an attacker to create Zerocoin spend transactions without a corresponding mint, resulting in the creation of about 370,000 Zcoins. Zerocoin discovered the bug when it noticed the total mint transactions did not match up with the total spend transactions. All but around 20,000 of the Zcoins were completely sold for around 410 BTC in profit. “Despite the severity of the hack, we will not be forfeiting or blacklisting any coins,” Zerocoin wrote in an announcement. “Trading will resume once pools and exchanges have had time to update their code. A new release will be pushed out pretty soon.”
These types of small issues continue to cause major issues for organizations. This past week also saw reports that a database belonging to digital publisher Ziff Davis could have been exfiltrated due to a website configuration issue affecting itmanagement.com, potentially exposing 7.5 million records. The database contained names, phone numbers, employment details, and email and employer addresses, as well as contact information for users registered on other Ziff Davis properties. Contact information for anyone in the shared database could have been viewed by incrementing or decrementing a field in a URL belonging to one Ziff Davis publication, according to multiple researchers.
There was also the discovery that more than 1.4 million emails sent over Harvard Computer Society (HCS) email lists were found to be public, including emails divulging Harvard students’ grades, financial aid information, bank account numbers for some student organizations, advance copies of a final exam, answer keys to problem sets, and more – likely since the default setting for HCS list archives was public. In addition, New York’s Stewart International Airport publicly exposed 760GB of server backup data for over a year due a network storage drive, which was installed by a contracted third-party IT specialist, that contained several backup images of servers and was not password protected.
The week’s incidents are yet another reminder that a good portion of effective cyber hygiene revolves around looking inward at an organization’s technology, policies, and procedures and their associated cyber risk.



 “The source code shows that Marble has test examples not just in English but also in Chinese, Russian, Korean, Arabic and Farsi,”
“The source code shows that Marble has test examples not just in English but also in Chinese, Russian, Korean, Arabic and Farsi,” 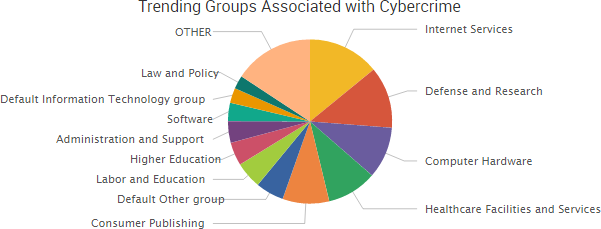
 The password manager LastPass has addressed a series of vulnerabilities that were discovered by Google Project Zero researcher Tavis Ormandy, including one now-patched “unique and highly sophisticated” client-side vulnerability in the LastPass browser extension.
The password manager LastPass has addressed a series of vulnerabilities that were discovered by Google Project Zero researcher Tavis Ormandy, including one now-patched “unique and highly sophisticated” client-side vulnerability in the LastPass browser extension. 
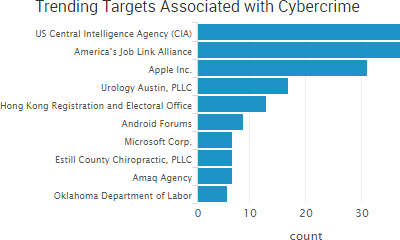
 “On February 20, 2017, a hacker created a job seeker account in an America’s JobLink (AJL) system,” the
“On February 20, 2017, a hacker created a job seeker account in an America’s JobLink (AJL) system,” the 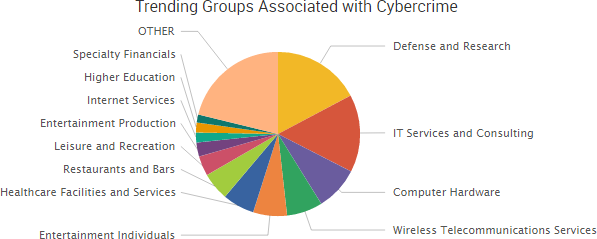
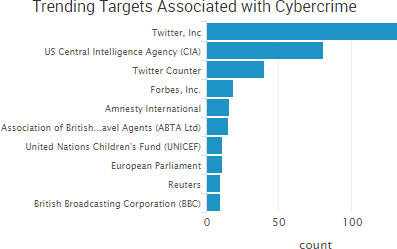
 One of the most profitable cybercriminal tactics is
One of the most profitable cybercriminal tactics is 
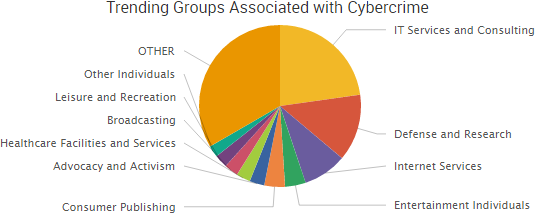
 Earlier this month, a patch was issued to address a high-impact vulnerability in Apache Struts Jakarta Multipart parser that allowed attackers to remotely execute malicious code. Shortly after the patch, an exploit appeared on a Chinese-language website,. Researchers then confirmed that attackers were “widely exploiting” the vulnerability. Since then, the issue has continued to affect numerous organizations through data breaches and service downtime.
Earlier this month, a patch was issued to address a high-impact vulnerability in Apache Struts Jakarta Multipart parser that allowed attackers to remotely execute malicious code. Shortly after the patch, an exploit appeared on a Chinese-language website,. Researchers then confirmed that attackers were “widely exploiting” the vulnerability. Since then, the issue has continued to affect numerous organizations through data breaches and service downtime.
 “Recently, the CIA lost control of the majority of its hacking arsenal including malware, viruses, trojans, weaponized ‘zero day’ exploits, malware remote control systems and associated documentation,”
“Recently, the CIA lost control of the majority of its hacking arsenal including malware, viruses, trojans, weaponized ‘zero day’ exploits, malware remote control systems and associated documentation,” 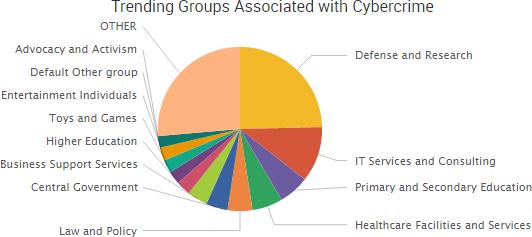
 Nearly every week researchers discover new data breaches due to publicly exposed databases that require no authentication, and this past week insecure Rync backups exposed the entire operation of River City Media (RCM), providing a rare glimpse inside what security researcher
Nearly every week researchers discover new data breaches due to publicly exposed databases that require no authentication, and this past week insecure Rync backups exposed the entire operation of River City Media (RCM), providing a rare glimpse inside what security researcher 



 Several companies have issued breach notification letters related to a malware incident at Aptos, Inc., which provides e-commerce solutions for a number of online stores. The breach at Aptos was discovered in November 2016, and notification by the various companies affected was delayed until recently at the request of law enforcement.
Several companies have issued breach notification letters related to a malware incident at Aptos, Inc., which provides e-commerce solutions for a number of online stores. The breach at Aptos was discovered in November 2016, and notification by the various companies affected was delayed until recently at the request of law enforcement. 
 “The bug was serious because the leaked memory could contain private information and because it had been cached by search engines,” wrote John Graham-Cumming, the CTO of Cloudflare, which provides performance and security services to numerous major websites. “We have also not discovered any evidence of malicious exploits of the bug or other reports of its existence.”
“The bug was serious because the leaked memory could contain private information and because it had been cached by search engines,” wrote John Graham-Cumming, the CTO of Cloudflare, which provides performance and security services to numerous major websites. “We have also not discovered any evidence of malicious exploits of the bug or other reports of its existence.”

 The Cloudflare bug can be traced back to a single character of code, which resulted in a buffer overrun, the company said.
The Cloudflare bug can be traced back to a single character of code, which resulted in a buffer overrun, the company said.
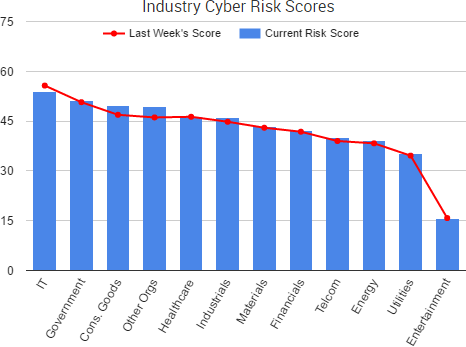 In addition to Yahoo, the past few weeks have seen several new regulatory announcements and fines related to data breaches.
In addition to Yahoo, the past few weeks have seen several new regulatory announcements and fines related to data breaches.
 Security researcher
Security researcher 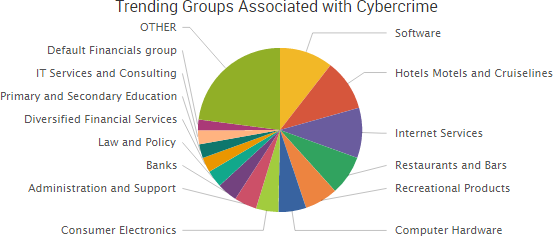
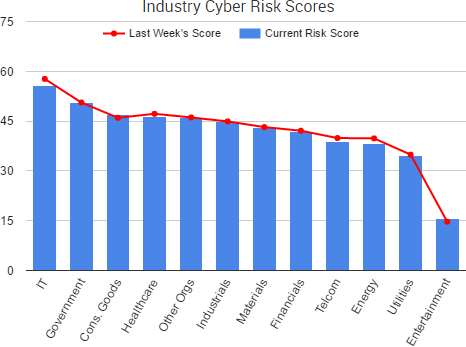 The past week saw the continuation of several stories highlighted in recent risk reports.
The past week saw the continuation of several stories highlighted in recent risk reports. 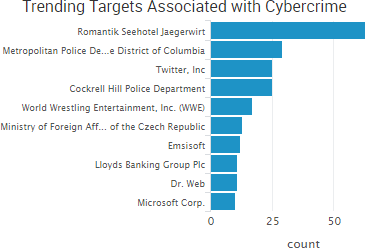 The Austrian hotel Romantik Seehotel Jägerwirt paid approximately $1600 in ransom after ransomware locked the hotel out of its computer systems and the hotel was unable to issue new key cards to arriving guests. The hotel’s reservation system was down for 24 hours; however, the initial media reports that customers were locked in their rooms due to the incident were false, the owner told
The Austrian hotel Romantik Seehotel Jägerwirt paid approximately $1600 in ransom after ransomware locked the hotel out of its computer systems and the hotel was unable to issue new key cards to arriving guests. The hotel’s reservation system was down for 24 hours; however, the initial media reports that customers were locked in their rooms due to the incident were false, the owner told 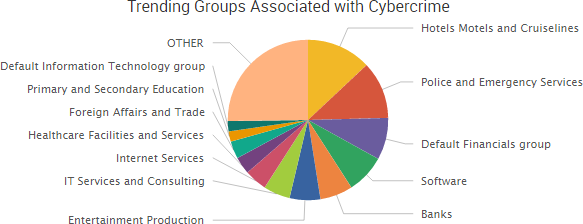
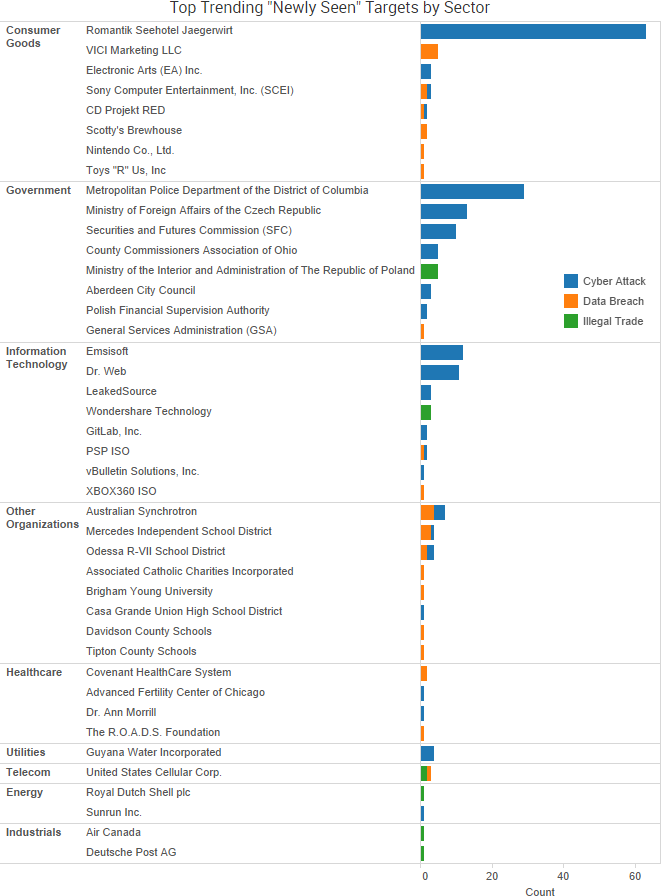
 The past week once again saw numerous organizations exposing data due to insecure public databases, and several of those databases reportedly contained data that was no longer in use.
The past week once again saw numerous organizations exposing data due to insecure public databases, and several of those databases reportedly contained data that was no longer in use.